Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.

Vitamin E for Acne: Is It Effective?
Vitamin E is a common antioxidant used in many skin care products. It’s also a popular natural remedy that’s added to many homemade skincare masks. It offers tremendous benefits for the skin. However, many people swear by the use of vitamin E oil for acne and rave about its acne-relieving properties. But does it really help against acne?
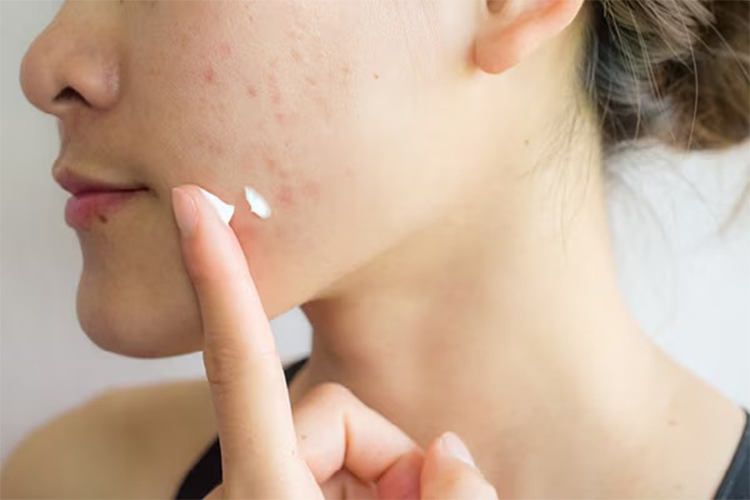

Is Vitamin E Effective For Acne? What the research says
Yes. Vitamin E oil is effective against acne, but it largely depends on how you use it. However, there is little clinical evidence supporting the topical effectiveness of vitamin E oil for acne and acne scars. There are some inconclusive studies, but they need further clinical evaluation:
One study found that applying a topical treatment with vitamin E oil before benzoyl peroxide (a drug used to treat acne) could improve the drug’s effectiveness and reduce acne (1). However, more research is needed to substantiate the results.
Another study found that a combination of vitamins A and E prevented the formation of comedones (small bumps commonly found on the forehead and chin of people with acne) and thus prevented the further growth of Propionibacterium acnes, which causes acne cause (2).
Some research suggests that taking vitamin E supplements or increasing your food intake may help reduce acne.
One study found that low levels of vitamins A and E in blood plasma can make acne worse (3).
Another study conducted on hairless mice found that both topical and oral vitamin E can help reduce UV-induced skin damage, inflammation, and pigmentation ( 4Trusted Source ).
Taking a combination of lactoferrin, vitamin E, and zinc by mouth has been found to reduce acne lesions within two weeks (5). However, more research is needed to draw a better conclusion about the benefits of vitamin E in acne treatment.
Vitamin E oil can work in combination with other ingredients and not just as a single treatment. Also, it’s not clear whether taking vitamin E supplements or applying them topically will work in any given case. This largely depends on your skin type and its response to vitamin E. Therefore, before using vitamin E or taking any supplements, it is important to learn which method is effective.
However, topical vitamin E can be used for anti-aging effects. It has been observed that the reactive oxygen species (free radicals) can alter the biosynthesis or production of collagen in the skin, thus accelerating skin aging (6). Vitamin E can act as a free radical scavenger and slow down the aging process.
There are many ways you can add vitamin E to your skincare routine to reduce acne. You can achieve this through products, foods, or supplements. We recommend consulting a doctor before figuring out which method to use.
Ways to use vitamin E for acne
1. Use vitamin E oil
Vitamin E is also available in cream, lotion, and serum forms. Many people squeeze the oil out of vitamin E capsules for topical use. The oil has a thick consistency, making it a good choice for people with dry and flaky skin as it acts as a moisturizer.
Apply this oil to your face while you sleep as it promotes the healing process of the skin during the night. You can apply the oil directly or mix it with your night cream. This DIY skin care can help in pimple prevention, skin rejuvenation and skin repair. You can also buy products that contain vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) as one of the ingredients. Such products are good for general care of your skin. Combined with soothing ingredients like aloe vera and rose water, it can soothe skin redness.
2. Vitamin E Supplements
Vitamin E supplements are available in capsule or tablet form. However, there is insufficient evidence to determine the proper dosage of vitamin E for both topical and oral use (6).
Consult a dermatologist before taking vitamin E supplements. This is because if you get enough vitamin E through food, you may not need to take additional supplements. The dermatologist can do a blood test to determine if you have a vitamin E deficiency.
Note: Vitamin E supplements can interact with medications. Talk to your doctor if you’re taking medication for another health problem.

3. Vitamin E through diet
Vitamin E occurs naturally in many foods. The richest sources of vitamin E are whole grains, spinach, nuts, sunflower oil, and olive oil (6). Consume foods like (7):
Nuts and seeds (peanuts, hazelnuts, almonds, sunflower seeds),
Vegetable oils (sunflower, safflower and wheat germ oil)
seafood
Green vegetables and fruits like spinach, broccoli, mango and kiwi
Consult a doctor to find out your recommended dietary dose of vitamin E. The amount of vitamin E you need depends on your age. However, people over the age of 14 (men, women, and pregnant women) need about 15 mg of vitamin E daily. If you’re breastfeeding, you may need up to 19 mg of vitamin E daily (7).
Using vitamin E (oil, capsules, or supplements) for acne just because it’s widely available can also lead to side effects.
Vitamin E for Acne: Possible Risks
Topical vitamin E is safe for the skin unless you are allergic to it. If you are allergic, it can irritate your skin and make existing symptoms worse. It can also cause contact dermatitis (8).
Some vitamin E oils contain certain types of preservatives and stabilizers (some brands mention them) that can irritate the skin. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not regulate vitamin E oil. This means that the same product from two different brands can have different concentrations and react differently on your skin.
Oils, creams, and serums containing vitamin E can feel a bit heavy on oily skin. If the product’s formula is oil based, it can lead to clogged pores and worsen acne. Therefore, before purchasing vitamin E products and dietary supplements for acne, carefully check the list of ingredients and the formula. Also, do a patch test and allergy test to avoid skin irritation and reactions.
Too high serum vitamin E levels may increase the risk of bleeding or bleeding in patients taking warfarin (an anticoagulant drug) (9).
Besides vitamin E, the dermatologist may suggest other over-the-counter treatments for effective acne treatment.
In summary, while there is some evidence that vitamin E may be effective against acne, more research is needed to fully demonstrate its benefits and effectiveness as a standalone treatment. It seems to work best in combination with other acne treatments or as part of an overall skin care routine.
Topical vitamin E oil can be applied directly to the skin or included in skin care products. However, it is important to watch out for possible allergic reactions or skin irritation. Those with oily skin should also be wary of using oil-based formulas, which can clog pores and worsen acne.
